NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Machine Learning for Smart Space-Based Radiation and X-Ray Spectrometer Instruments
This student team worked to apply machine learning algorithms to the space-based operation and calibration of two small instruments that are planned to fly on a CubeSat mission in the 2024 timeframe. The instruments generate time-series data streams at the output based on physical properties measured at their respective inputs. The challenge this student team worked to address is to convert these time series data streams into useful information that is: 1) reliably reproduceable and related to actual physical properties being measured, and 2) to calibrate the information such that error is either known or bounds can be placed on the information. The student team was able to work to utilize the dynamic environment, both the physical parameters being measured and the environment the sensor operates in (e.g., space environmental factor such as temperature) as models to more accurately use the raw data to infer actual physical property being measured. Machine Learning is a technique that has been used successfully in these type of application in the past, and this student team was encouraged to explore the use for these two sensors. A desired outcome this student team worked to accomplish was to demonstrate machine learning algorithms to autonomously calibrate time-series outputs from two instrument, radiation sensor and x-ray spectrometer, based on the space environment the sensors will operate in. In other words, software that will convert raw data streams from the instruments into useful calibrated information.
Faculty Adviser(s)
Payman Arabshahi, Electrical & Computer Engineering
Related News
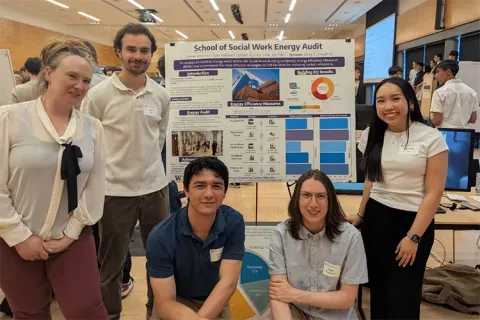
Mon, 10/13/2025 | UW Mechanical Engineering
Capstone collaboration leads to award
An ME capstone team received first place for its energy audit of the UW School of Social Work building.

Mon, 07/07/2025 | UW Mechanical Engineering
Capstone creations
Students displayed innovative capstone design projects at the 2025 expo.

Fri, 09/20/2024 | UW Civil & Environmental Engineering
Smarter irrigation for a greener UW
A new project combines satellite data with ground sensors to conserve water and create a more sustainable campus environment.

Mon, 09/09/2024 | UW Mechanical Engineering
Testing an in-home mobility system
Through innovative capstone projects, engineering students worked with community members on an adaptable mobility system.